
How Influencers Became Key to Big Brands During the Pandemic — and Why They’ll Continue to Grow
Sam Blake 11.30.20 | Link to Article
- Influencer marketing has surged during the pandemic as more consumers have moved online and brands have been forced to adapt to new challenges.
- The rise of ecommerce and social media continues to usher in a wave of less formal and potentially cheaper marketing from online icons directly connected to audiences that brands can target.
- Marketers expect the trend to continue, which could lead to more unexpected brand partnerships, like a KFC line of Crocs or Forever 21’s Cheetos apparel.
Mix together a cup of cold brew, three pumps of caramel syrup, a splash of whole milk and a generous portion of TikTok and you’ve got yourself “The Charli” – Dunkin’ Donuts’ new menu item promoted in partnership with Charli D’Amelio, a superstar social media influencer and the drink’s namesake.
Influencer marketing campaigns are not new, but the coronavirus pandemic has accelerated their appeal as companies have been forced to ramp up their online presence. Marketers expect that to continue, due to a combination of changing consumer behavior, a growing sophistication of data and analytics, and tighter ad budgets.
As these forces take shape, subscription streaming services expand and cable’s decline continues, could it spell the end of TV commercials?
The Rise of Influencer Marketing
Fundamentally, an influencer is someone with a level of knowledge, expertise or social following that enables them to, well, influence other people’s decisions. That premise has existed for a long time, but the internet and social media gave rise to a new capability for companies to target specific audiences with more precision than a television or radio commercial. As a result, niche, direct-to-consumer businesses offering specific products, and online influencers to peddle those products, have bloomed.
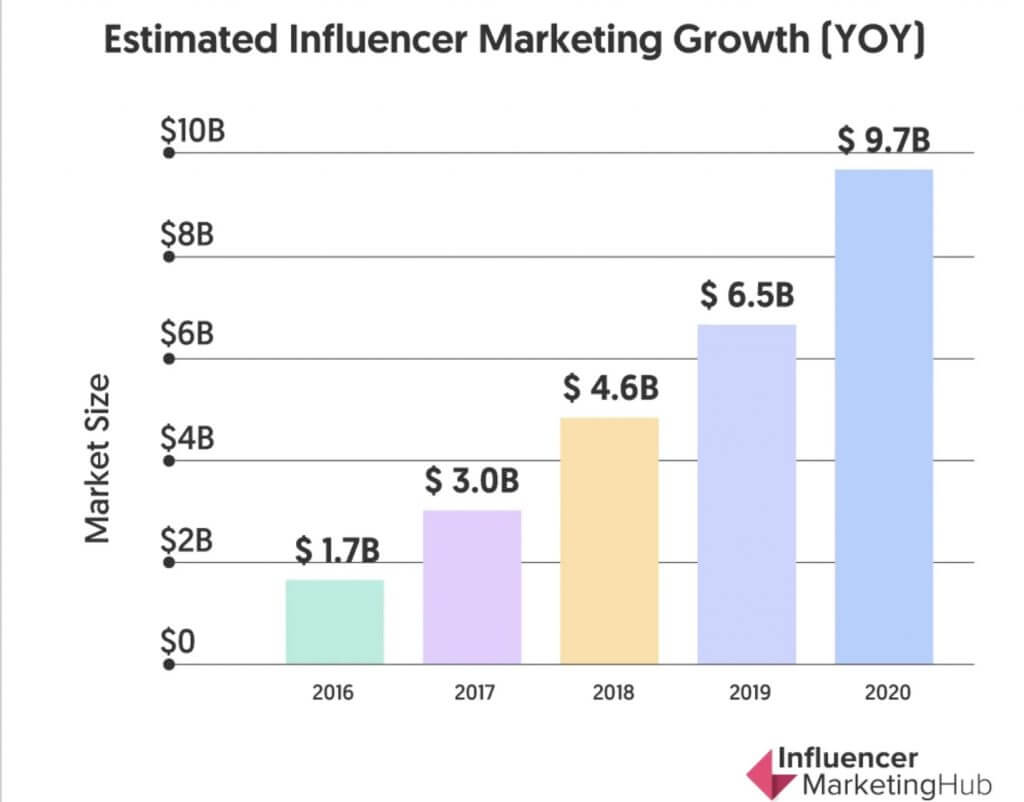
Before the pandemic set in, Influencer Marketing Hub, a research firm, reported influencer marketing was expected to grow to a $9.7 billion business in 2020, nearly a 50% increase from 2019. More recent evidence suggests that companies are still piling in, even faster than predicted.
In the quarter from June through August, for example, across a sample of 4,500 ecommerce retailers, sales and customers driven to brands’ websites through YouTube influencers are up 80% year over year, according to MagicLinks, an L.A.-based social media marketing company that helps firms track the performance of their influencer campaigns. Applications from influencers wishing to use MagicLinks’ sales tools have grown nearly fivefold from the start of the pandemic. And across MagicLinks’ retail customers, which include the likes of Walmart, Target, L’Oreal and Best Buy, influencer-driven sales are up 115%.
Several other marketing agencies also told dot.LA they’ve seen increased spending on influencer content, and an expansion of the types of companies that use influencer marketing, compared to pre-COVID.
Part of that is out of necessity. With film production shut down due to the pandemic, traditional commercial advertising was hampered. And with marketing budgets crimped, potentially cheaper advertising routes, such as a well-targeted influencer campaign, grew more attractive.
Influence in the Wake of Ecommerce
The pandemic has also caused ecommerce to skyrocket and led people to spend more time on social media, both of which have increased the supply of potential customers for brands to target with influencers.
“Consumers crave real-life stories and authenticity, and influencers are able to highlight brands in a way that feels real and accessible. We are seeing that during the pandemic, this need is further heightened as more consumers are spending more time on social platforms,” Grubhub’s director of content and social Mandy Cudahy told dot.LA.
The growing sophistication of data and analytics on the effectiveness of influencer marketing has also helped companies create more targeted ad campaigns likely to reach spenders. For example, tools are improving to help brands find the right influencer, track their ability to drive purchases, and even predict how well an influencer campaign will do.
“There’s been a much bigger push around nailing down the attribution and ROI,” said Kevin Gould, co-founder of three L.A.-based ecommerce brands that rely heavily on influencer marketing and collectively earn over $60 million in annual revenue.
That push, in turn, is helping to nudge brands that have historically shied away from influencer marketing. Part of what has held them back is the fact that the data from traditional channels like television and radio advertising is far more robust than what’s available in the influencer space, if only because it is relatively new.
“You’re going up against hard sets of data since like the birth of Macy’s, so it didn’t become a priority,” said Jennifer Piña, MagicLinks’ director of brand partnerships. “Now it’s being forced to become a priority.”
As a result, bigger, more traditional brands are moving into what has until now been a channel primarily used by smaller, direct-to-consumer brands. Tito’s Vodka, for instance, ran its first influencer campaign in August with Brooklyn-based First Tube Media. Prior to the campaign, “Tito’s had never spent a dollar in influencer marketing,” First Tube CEO Andrew Beranbom told dot.LA. Superdry, a publicly-traded British clothing company founded in 1985, is partnering with MagicLinks to launch its first large influencer campaign in advance of the holiday season.
How Influencers Change What We Buy, and What They Make
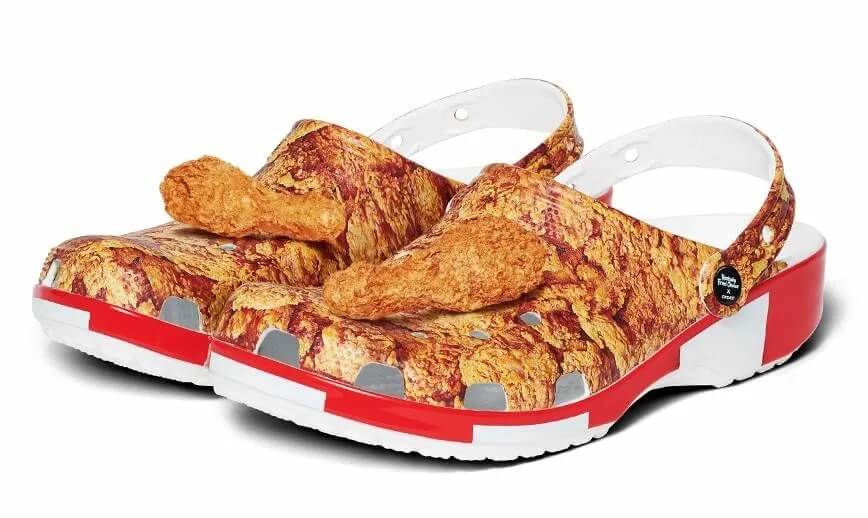

Influencer marketing has also given rise to new partnerships between brands that arguably have nothing to do with each other, with influencers as the linchpin linking them together. Examples include a KFC line of Crocs, e.l.f. Cosmetics’ Chipotle burrito-inspired handbag and makeup kit, and Forever 21’s Cheetos apparel line.
“It’s this idea of like, a brand is a brand,” said Piña. “What they actually sell or what people purchase from them is oftentimes irrelevant. It’s more about the packaging and the moment and the feel and that’s what social media does: it creates excitement for something that is not necessarily exciting. Like Crocs: Crocs is like your dad’s brand. But it can immediately become cool, at the drop of a pin, once you get the right influencers involved.”
Even as data attribution improves and consumers spend more time online in the land of influencers, one key downside to influencer marketing remains: limited control. A company can manage every element of a commercial shoot or Facebook ad, but using an unscripted TikTok or Instagram influencer requires letting go.
“Brands in some categories historically have been super fearful of letting influencers tell their story because it is so important to the sanctity of the brand to keep the messaging really succinct and in line with the brand guidelines,” Piña said.
Yet that informality is part of the appeal of influencer marketing.
“Brands get stuck on needing to be perfect or scripted, whereas influencers talk to you like they’re your next-door neighbor,” said Brian Meert, chief executive of L.A.-based AdvertiseMint, a digital advertising agency. “It’s very organic; it doesn’t feel like a pushy ask. I think those kinds of elements have enabled us to grow sales for our clients using more of these influencer- and consumer-generated type videos.”
Piña noted that while Ralph Lauren, a premium fashion retailer, has been wary of using influencers because of “brand safety,” the company recently approached MagicLinks to build out a year-long TikTok strategy. Even as the social video giant’s fight with the White House threatened to upend the living of its influencers, TikTok’s hold on the traditionally elusive younger demographic – along with other user-generated video platforms like Instagram, YouTube, Twitch and Snap – has become increasingly hard for companies to ignore.
“Any brand that wants to connect with Gen Z, and sell whatever product or service they have, has to engage (with these platforms),” said Glenn Ginsburg, SVP of global partnerships at influencer marketing agency The QYOU. “Moving forward I think we’ll see brands start to build deeper relationships with influencers.”
Not every brand is poised to get the same value from an influencer campaign, however. An influencer is unlikely to save the day for a travel and tourism company ravaged by the pandemic, for instance. And it remains a challenge to reliably execute an influencer campaign, notwithstanding the emergence of new tools to do so.
“A lot still depends on relationships, conversations and trial and error,” said Darren Litt, chairman and co-founder of L.A.-based talent marketplace MarketerHire. “A successful influencer campaign requires a detailed understanding of an influencer’s brand, and that’s hard to do with tech and AI alone.”
Achieving the cost-efficiency of a well-targeted campaign also remains most viable for companies that are best positioned to drive online purchases. Using Kim Kardashian to sell clothing that flatters one’s figure, for example, is more likely to drive trackable sales than, say, pushing Pepsi.
“For mass-market products looking to reach a broad audience, TV advertising remains effective because you get the upside of wide reach with the downside of limited targeting,” said Litt. That’s especially true for products that people don’t typically purchase online.
But much like a song that goes viral on TikTok can drive a listening bump on streaming platforms like Spotify, so, too, it appears, can an influencer campaign drive offline purchases.
After all, Dunkin’ Donuts saw sales surge following its D’Amelio partnership, even though the girl with over 100 million TikTok followers has reportedly never ordered “The Charli” herself.
